Publications
Lmod: A large multimodal ophthalmology dataset and benchmark for large vision-language models
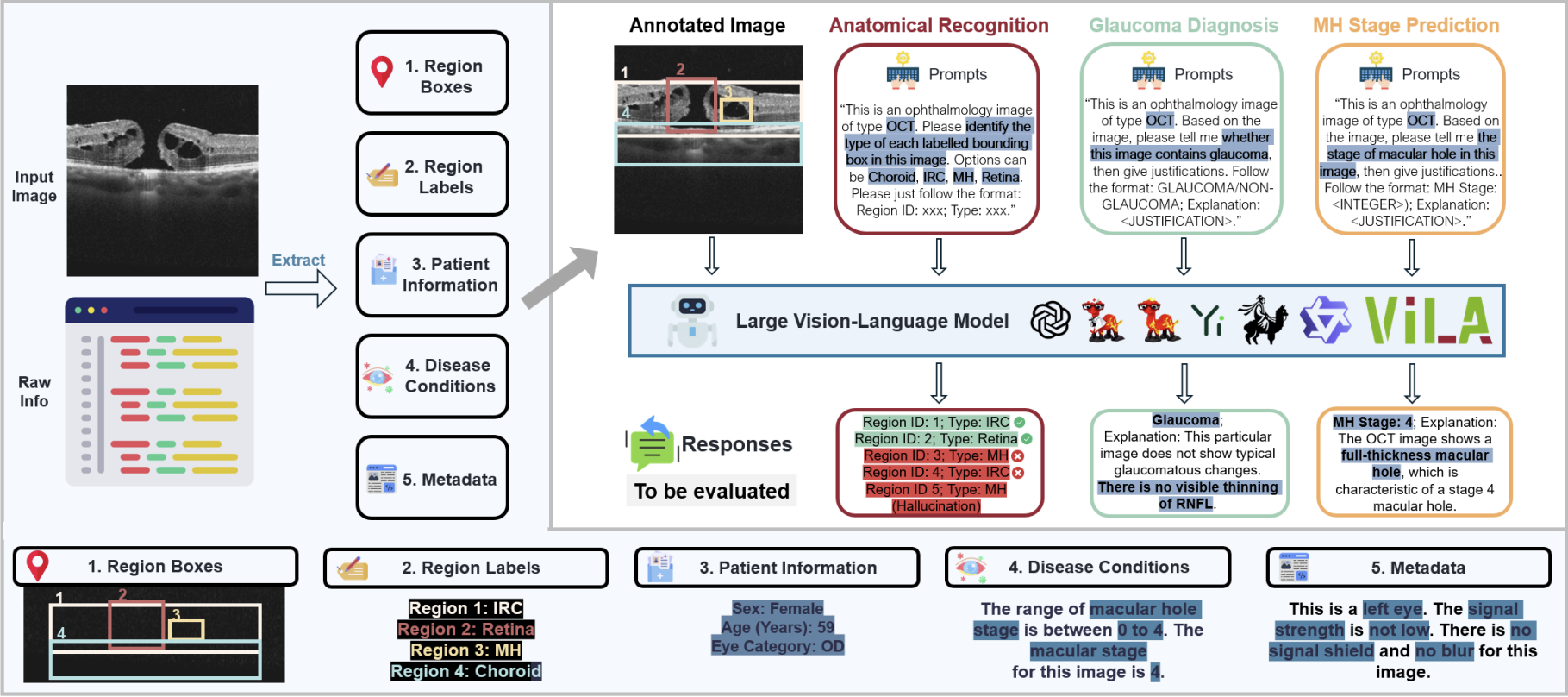
Abstract: The prevalence of vision-threatening eye diseases is a significant global burden, with many cases remaining undiagnosed or diagnosed too late for effective treatment. Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have the potential to assist in understanding anatomical information, diagnosing eye diseases, and drafting interpretations and follow-up plans, thereby reducing the burden on clinicians and improving access to eye care. However, limited benchmarks are available to assess LVLMs' performance in ophthalmology-specific applications. In this study, we introduce LMOD, a large-scale multimodal ophthalmology benchmark consisting of 21,993 instances across (1) five ophthalmic imaging modalities: optical coherence tomography, color fundus photographs, scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, lens photographs, and surgical scenes; (2) free-text, demographic, and disease biomarker information; and (3) primary ophthalmology-specific applications such as anatomical information understanding, disease diagnosis, and subgroup analysis. In addition, we benchmarked 13 state-of-the-art LVLM representatives from closed-source, open-source, and medical domains. The results demonstrate a significant performance drop for LVLMs in ophthalmology compared to other domains. Systematic error analysis further identified six major failure modes: misclassification, failure to abstain, inconsistent reasoning, hallucination, assertions without justification, and lack of domain-specific knowledge. In contrast, supervised neural networks specifically trained on these tasks as baselines demonstrated high accuracy. These findings underscore the pressing need for benchmarks in the development and validation of ophthalmology-specific LVLMs.
Augmenting biomedical named entity recognition with general-domain resources
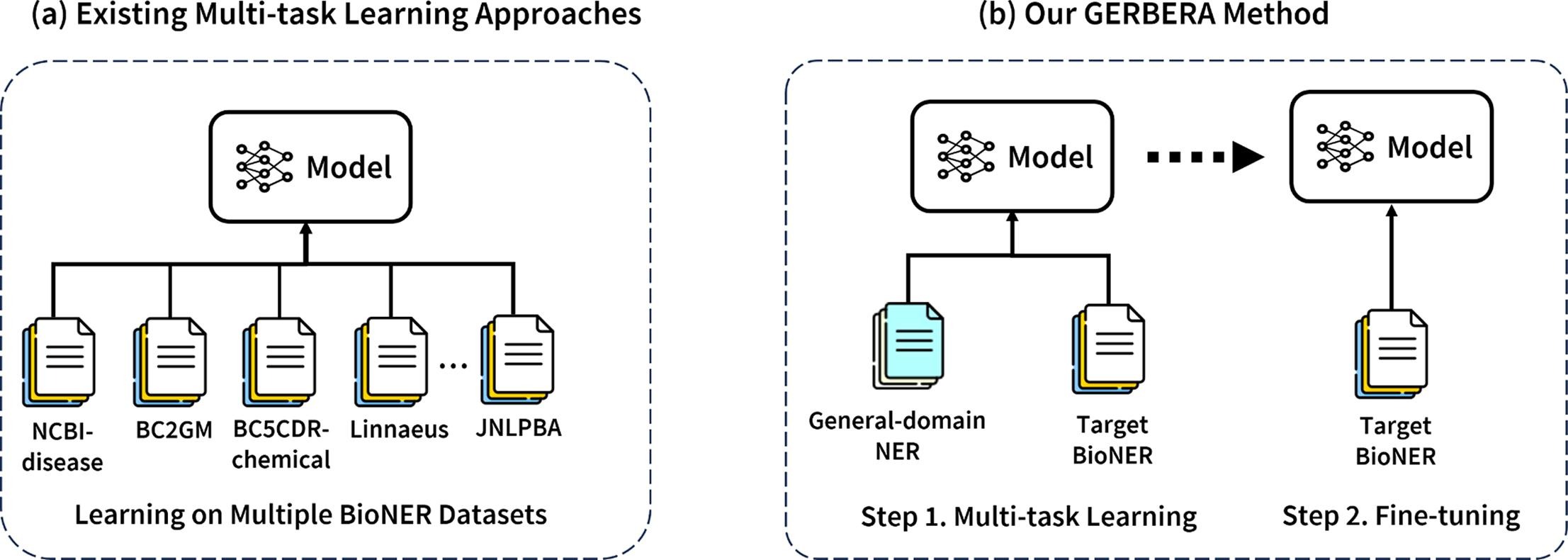
Abstract: Training a neural network-based biomedical named entity recognition (BioNER) model usually requires extensive and costly human annotations. While several studies have employed multi-task learning with multiple BioNER datasets to reduce human effort, this approach does not consistently yield performance improvements and may introduce label ambiguity in different biomedical corpora. We aim to tackle those challenges through transfer learning from easily accessible resources with fewer concept overlaps with biomedical datasets. We proposed GERBERA, a simple-yet-effective method that utilized general-domain NER datasets for training. We performed multi-task learning to train a pre-trained biomedical language model with both the target BioNER dataset and the general-domain dataset. Subsequently, we fine-tuned the models specifically for the BioNER dataset. We systematically evaluated GERBERA on five datasets of eight entity types, collectively consisting of 81,410 instances. Despite using fewer biomedical resources, our models demonstrated superior performance compared to baseline models trained with additional BioNER datasets. Specifically, our models consistently outperformed the baseline models in six out of eight entity types, achieving an average improvement of 0.9% over the best baseline performance across eight entities. Our method was especially effective in amplifying performance on BioNER datasets characterized by limited data, with a 4.7% improvement in F1 scores on the JNLPBA-RNA dataset. This study introduces a new training method that leverages cost-effective general-domain NER datasets to augment BioNER models. This approach significantly improves BioNER model performance, making it a valuable asset for scenarios with scarce or costly biomedical datasets.
